Almost!
Tomorrow is the first day of spring (insert “Where has this year gone?” or similar comment here)! So, what better time to have a look at what is happening in the vineyard.
Pinot Noir
Over at his Charleston vineyard, Kim Anderson is currently restructuring the Pinot Noir. Although it is more expensive way to prune, he is converting it from spur-pruned to cane-pruned.
Cast your mind back to our post about pruning to understand the differences between the two.
Why would he do that?
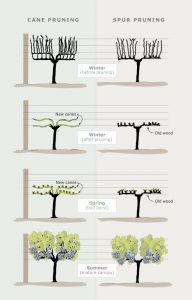
There are a couple of good reasons to do this…
- The shoots burst more evenly and have a predominance of fruitful buds (not so many blind or fruitless shoots).
- It creates a more open canopy with the shoots more evenly spaced and less likelihood of fruit occurring in clumps. This is important because fruit which is close together rub against each other and spread disease.
- If the old arms are removed each year, then there will be less pressure from scale insects and eutypa dieback (a fungal disease).

It often becomes a necessary job anyway when spur positions get damaged and then leave large gaps along the thick horizontal branches(cordon arm) – as you can see in this photo.
This vine is half converted – it is still spur-pruned on the left side of the “V” (or crown – which is much more pronounced on the vines behind).
Kim cuts the old cordon wires where he can get at them, then cuts through the cordon arms of the vine leaving a cane on each half of the crown. The right half shows a single cane left to wind onto the new wire when it comes. The old wire is often stuck in the crown which means that he must pull the wire through the twisted arms of the vine with pliers (those red things that are grabbing onto the wire!).
As you can guess cane pruning and restructuring are both very time-consuming and expensive to perform but the hope is that it will result in superior wine as a result.
Chardonnay and Sauvignon Blanc
Both these varieties have been cane-pruned already and are waiting for bud burst.
Bud burst refers to the period in early spring during which grapevines, which have been dormant through the winter, first begin to produce new shoots. If you would like to learn more about bud burst dormancy, check out this article – it’s a fascinating topic.
Bud burst may be a bit earlier than usual this year due to the warm days we’ve had over the past few weeks – although a lot of mornings have been below zero.
So, other than that, there is nothing really to do in the vineyard while the vines are dormant, right?
Wrong!
It is surprising just how much work goes into making sure the vines are in good health before vintage begins again.
Kim has been super busy spraying the broadleaved weeds to ensure the only thing left in the vineyard is nice grass. He has also begun under vine spraying and slashing. Together, this helps to reduce the risk of frost damage.
Short grass provides some heat whereas long grass reduces heat uptake from the sun and causes the frost layer to ride higher as it flows down the slope.
The next job on his to-do list is to clean the frost sprinklers which only have around 6,000 heads! He’ll then get to work on fixing any posts which have been broken by machinery during the year.
And the list goes on…
The birth of new things…
With spring symbolising themes of rebirth and renewal, what better time for us to introduce our beautifully updated website!
Watch out for an email tomorrow directing you to our fresh new look site where you can read, learn and shop all things Somerled.
In the meantime, here is a sneak peak!
I have also incorporated this blog into our new site. So, this address (www.somerledwinesseries.com) will no longer be updated. If you have bookmarked this site, please change it to www.somerled.com.au (remember if you head there now, it will still be our old site… the new one will be there tomorrow!) to keep up to date with our latest posts.

 Remember that place we got all the grapes from?
Remember that place we got all the grapes from?